Table of contents

What Is Supplier Performance Management?
At its core, Supplier Performance Management SPM is the systematic process of evaluating, monitoring, and enhancing supplier performance. It transcends mere transactional interactions, aiming to foster long-term partnerships that drive mutual success.
Why Does SPM Matter?
- Quality Assurance: SPM ensures that suppliers consistently meet quality standards. Whether it’s raw materials, components, or finished products, maintaining high-quality levels is non-negotiable.
- Timely Delivery: On-time delivery is the lifeblood of supply chains. Supplier Performance Management helps track lead times, reduce delays, and mitigate disruptions caused by unforeseen events.
- Cost Optimization: Effective SPM identifies cost-saving opportunities, streamlines procurement processes, and encourages competitive pricing.
- Risk Management: By assessing supplier risk, organizations can proactively address vulnerabilities and build resilient supply chains.
- Supplier Relationships: SPM cultivates collaborative partnerships that extend beyond simple transactions; it revolves around building trust, fostering transparency, and striving towards shared goals.
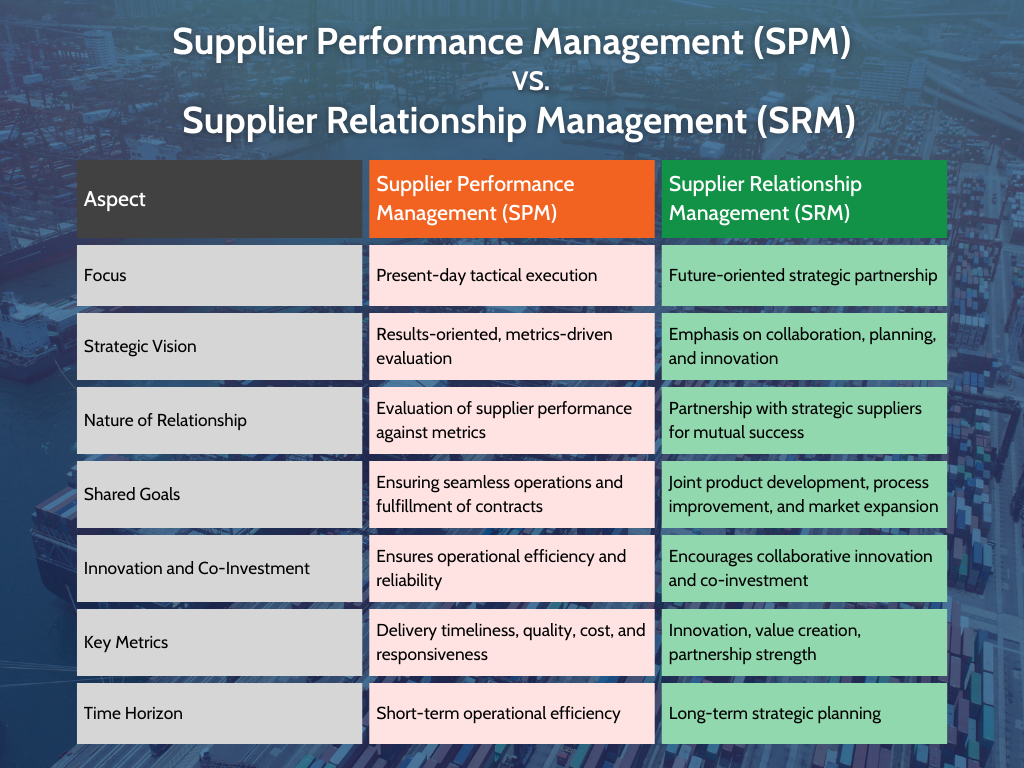
How Supplier Performance Management Differs From Supplier Relationship Management
Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
At the heart of SRM lies a strategic partnership, a harmonious collaboration between organizations and their key suppliers. It goes beyond simple transactional exchanges. Here’s what sets it apart:
Strategic Vision: Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) is looking towards the future. It requires collaboration in planning, fostering innovation, and creating value together. Organizations invest in building strong partnerships with strategic suppliers to help drive their success.
Shared Goals: SRM isn’t just about products; it’s about shaping the future together. Suppliers become partners in product development, process improvement, and market expansion. They contribute ideas, share risks, and invest in mutual growth.
Innovation and Co-Investment: Strategic Relationship Management (SRM) fosters a culture of collaborative innovation and emphasizes forming partnerships to drive groundbreaking advancements. When a supplier shares your R&D objectives, that’s when the essence of true SRM shines through.
Supplier Performance Management (SPM)
SPM, in contrast, is more tactical and results-oriented. While SRM looks at the big picture, SPM zooms in on execution:
Metrics-Driven Evaluation: SPM assesses supplier performance based on measures like delivery timeliness, quality, cost, and responsiveness. The goal is to ensure that suppliers fulfill their contractual duties effectively.
Operational Efficiency: Supplier Performance Management (SPM) is the key to ensuring seamless operations. When a supplier is reliable, produces high-quality products, and works efficiently, it benefits the entire ecosystem. Think of it as the essential lubricant that keeps the supply chain machinery running smoothly.
Tactical Focus: SPM is all about efficient execution in the present day. It involves ensuring production schedules, effectively managing inventory, and reducing disruptions. SPM shines through when the company ensures shipments arrive punctually, upholds quality standards, and keeps costs in check.
Benefits of Effective SPM
- Cost Savings: Streamlined processes lead to cost reductions and better negotiation outcomes.
- Supply Chain Resilience: SPM mitigates risks, ensuring continuity even during disruptions (natural disasters, geopolitical shifts, etc.).
- Service Quality: High-performing suppliers enhance service levels, directly impacting customer satisfaction.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient supply chains translate to smoother operations and improved bottom lines.
- Financial Stability: Assessing supplier financial health contributes to overall stability.
Three Phases of Supplier Performance Management
Let’s explore the three critical phases that organizations navigate to ensure a steady and reliable supply of materials while maintaining strong supplier relationships:
1. Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
In the beginning, organizations establish goals and measure supplier performance using specific metrics or KPIs. Key steps include:
- Defining Performance Targets: Organizations align KPIs with strategic goals. KPIs help suppliers perform well by guiding them on delivery, quality, cost savings, and compliance.
- Agreeing with Suppliers: Transparent communication is crucial. Organizations collaborate with suppliers to agree upon performance targets. These targets become the yardstick for ongoing evaluation.
2. Monitoring and Assessing Performance
During this active phase, we regularly check suppliers’ performance against set goals and metrics. Key activities include:
- Regular Performance Reviews: Organizations use scorecards, dashboards, and other tools to track supplier performance. Are they meeting quality standards? Delivering on time? Staying within cost parameters?
- Root Cause Analyzing: When performance falls short, organizations dig deeper. Why did that shipment arrive late? What caused the quality issue? Identifying root causes enables corrective actions.
- Feedback Loops: Engage in candid conversations with suppliers. Seek their feedback on processes, communication, and collaboration.
3. Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
This phase is about agility and evolution. Organizations strive for ongoing improvement and adapt to changing dynamics. Key aspects include:
- Kaizen Philosophy: SPM isn’t static. Continuous improvement is the mantra. Look for opportunities to enhance supplier performance.
- Benchmarking: Compare supplier performance against industry benchmarks. Identify areas where you can leapfrog ahead.
- Flexible Governance: As markets shift and disruptions occur, governance processes should adapt. Collaborate across functions—procurement, quality, logistics—to enhance decision-making.
Implementing Effective SPM: Best Practices
1. Define Clear Metrics (Going Beyond the Basics)
- Holistic Metrics: While on-time delivery and quality are fundamental, consider broader metrics.
- Responsiveness: How quickly does the supplier address inquiries or resolve issues?
- Risk Mitigation: Assess the supplier’s ability to handle disruptions (natural disasters, geopolitical shifts, etc.).
- Financial Stability: Evaluate their financial health to ensure long-term viability.
- Customize Metrics: Tailor metrics to your industry, product type, and business model. A high-tech electronics supplier may have different critical metrics than a food packaging supplier.
2. Regular Performance Reviews and Feedback (Beyond the Scorecard)
- 360-Degree Feedback: Engage in candid conversations with suppliers. Seek their feedback on your processes, communication, and collaboration.
- Root Cause Analyzing: Why did that shipment arrive late? What caused the quality issue? Address root causes systematically.
3. Monitor Supplier Performance Data (Beyond Automation)
- Predictive Analytics: Leverage data not just for historical tracking but also for predictive insights. Can you anticipate supply chain disruptions based on early warning signs?
- Benchmarking: Compare supplier performance against industry benchmarks. Identify areas where you can leapfrog ahead.

30+ Audit and inspection checklists free for download.
4. Continuous Improvement and Recognition (Beyond Compliance)
- Kaizen Philosophy: SPM is about continuous improvement. Encourage suppliers to adopt the same mindset.
- Supplier Recognition Programs: Acknowledge high-performing suppliers publicly. It motivates them and sets a positive example for others.
5. Flexible, Streamlined Governance (Beyond Policies)
- Agile Governance: Governance isn’t about rigid policies; it’s about agility. As markets shift, regulations change, and disruptions occur, your governance processes should adapt.
- Collaborative Governance: Involve cross-functional teams—procurement, quality, logistics—in supplier management. Their collective insights enhance decision-making.
Best Supplier Performance Management KPIs and Metrics
Supplier Performance Management success relies on clear metrics and KPIs. These help organizations improve supplier relationships, ensure quality, and achieve operational success. Here are the crucial KPIs and metrics that pave the way for a thriving SPM strategy.
- Lead Time
- Defect Rates
- Regulatory Compliance
- Contract Compliance
- Customer Service
- Risk Factor
- On-Time Delivery
- Order Accuracy
- Return on Investment (ROI)
A Solution to Better Supplier Management
Certainty specializes in enterprise-level inspection and audit software solutions designed to improve performance and sustainability. Their robust platform empowers organizations to assess and manage supplier performance effectively. Here’s how Certainty contributes to supplier performance management:
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Certainty enables easy collection and reporting of inspection data. Whether online, offline, in the field, or on the shop floor, users can complete audits and inspections wherever needed. This flexibility ensures accurate and consistent data capture across the business.
- Real-Time Reports: With Certainty, organizations gain access to real-time performance reports. These reports provide insights into supplier performance metrics, allowing timely decision-making. Whether it’s safety inspections, quality audits, or supply chain compliance assessments, Certainty delivers actionable information.
- Issue Resolution on the Go: When issues are identified, Certainty streamlines the resolution process. Users can create and delegate actions directly within the platform. This on-the-go issue management promptly addresses identified supplier issues.
- Supplier Scorecards: Certainty’s reporting tools allow for consistent, comparable, and accurate supplier metrics. Organizations can track supplier performance over time, highlight good practices, and identify areas that need improvement. Supplier scorecards become powerful tools for ongoing evaluation.
- Business Insights: By collecting, tracking, and reporting accurate data, Certainty provides detailed business insights. These insights empower teams to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and enhance overall performance and sustainability.
Organizations worldwide trust Certainty Software to complete millions of accurate audits and inspections annually. We help enterprises improve in safety, quality, ESG, and Supply chain performance management. Book a demo with our team today to learn how Certainty can help your enterprise-level challenges.



