What is the HACCP Checklist?
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) Checklist provides a systematic and preventative approach to food safety regarding biological, chemical, and physical hazards. This 82-question checklist is essential for ensuring corrective actions are being taken throughout each step of the food production process and that the HACCP system is being followed.

We help make your HACCP inspections a success.
Download the HACCP Food Safety Checklist
What the Checklist Includes
Covered in the checklist template include some of the following:
- Personal hygiene
- Food preparation
- Hot/cold holding
- Refrigeration
- Food and dry storage
- Cleaning and sanitizing
- Utensils and equipment
- Garbage and disposal
- Pest control
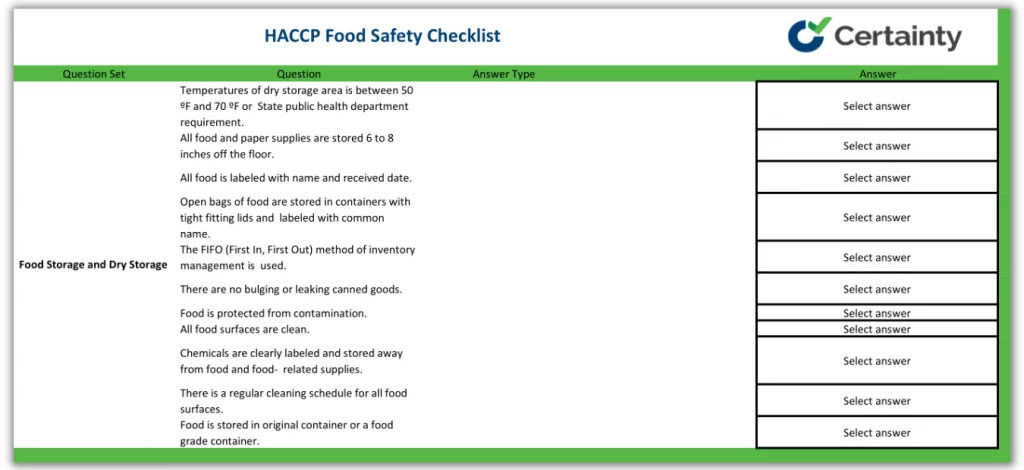
Before undertaking the HACCP checklist into a current food process, it is highly recommended to develop a HACCP plan which follows the HACCP principles. Internal audits should be scheduled regularly to ensure each step of the plan is successfully accomplishing its goal.
The HACCP Plan
Formulating a HACCP Plan ensures that preventative measures are identified regarding food safety measures. HACCP plans can be generic templates, but any unique conditions regarding aspects of the plan during development need to be considered. While developing a plan may at first seem intimidating, a step-by-step general guide has been designed to assist in building a plan.
1. Formulate a HACCP team
Building a strong HACCP team is the foundation of an exceptional plan. These internal team members should be carefully selected from differing fields of the food business such as quality assurance, engineers, and machine operators. Team members from different fields and experiences within the production process allow for a better representation of the entire process from harvest to consumption. It is vital to train these members on the HACCP system as well as to maintain up-to-date training records for plan success.
2. Describe the food and its distribution
Here, the ingredients and raw materials within the food products should be identified. In addition, how the food is transported and stored such as if the product(s) are refrigerated, room temperature, a specific temperature range, or any other circumstances should be included in the HACCP Plan.
3. Define the consumers of the food and its intended use
Understanding and recording the primary consumer of the product(s) is essential to a well-developed plan. These can include children, adults, seniors, or even specific groups such as vegetarians, vegans, immunocompromised, etc. Consideration should also be taken into not only the primary consumer base but also consumer groups that deviate from the intended targeted audience. For example, meal replacement drinks are typically intended for seniors to ensure they receive their daily nutritional needs; however, middle-aged adults also purchase these products for personal consumption.
4. Build a flow diagram
Constructing a flow diagram clearly illustrates an entire food process and provides a clear and concise understanding for all employees. The benefits of building a flow diagram are that it helps to mitigate any confusion at any process step.
5. Verify and update the flow diagram
General reviews of these processes will need to be updated by the HACCP team. As processes are implemented and time progresses, areas of improvement may present themselves and it’s important for the team to continuously review the process and adjust the flow diagram accordingly.
The 7 Principles of HACCP
To ensure that the HACCP plan meets its intended use, there are seven basic principles recommended to follow when creating this plan.
1. Hazard analysis
A hazard analysis will identify any potential hazards associated with the food product(s). These risks include biological, chemical, and physical hazards.
Biological hazards are hazards produced by an organism and include viruses, parasites, mold, etc.
Chemical hazards include food cleaning products, pest control substances, and other cleaning agents.
Physical hazards pertain to instances of foreign objects being introduced into a food product such as metal, or natural physical hazards such as bones.
2. Identify critical control points
Areas, where control is possible to apply at any food production stage and is crucial at preventing a food safety hazard, are defined as critical control points (CCP).
3. Determine critical limits
Recording the minimum and maximum critical limits of control to prevent hazards assists in determining whether conditions are safe or unsafe.
4. Monitoring procedures
Continuous observation and recording of procedures provide validation of consistency in ensuring critical control points are within the safe allowance of the critical limits set.
5. Corrective actions
If there is a failure to control the limits identified, a set of predetermined actions should be formulated and acted on accordingly.
6. Verification procedures
In ensuring preventative rather than reactive actions are taken to ensure HACCP system success, verification and review of the plan and systems in place should be undertaken regularly.
7. Record-keeping and documentation
It is important to centralize the documentation of the HACCP system and should include the hazard analysis, the HACCP plan, a HACCP summary, and additional support material.
How Certainty Improves HACCP Inspections
Using Certainty Software, performing HACCP food safety inspections becomes easier and generates better actionable information. Whether using our checklist templates or creating your own unique forms, Certainty gives its users the freedom and customizability to support every company’s unique inspection and auditing needs.
Reporting checklist findings at an enterprise-wide level can be filtered to your needs by options such as inspection type, users, site, region, question, or answer. Within your configurable dashboard, you can track issues identified, set up automated notifications and actions, and so much more.
For more on Safety Inspection solutions, click here.
To download this checklist please complete the form below.



